Humabs BioMed (Switzerland), in collaboration with institutional partners has succeeded in isolating new antibodies against the Ebola virus and turned them into a potential therapy against it.
 Humabs discovers monoclonal antibodies by doing blood analysis of survivors to given infectious diseases. For example, if one wants the cure for the flu, it looks into people who recuperated from it and what antibodies they have developed against it.
Humabs discovers monoclonal antibodies by doing blood analysis of survivors to given infectious diseases. For example, if one wants the cure for the flu, it looks into people who recuperated from it and what antibodies they have developed against it.
This strategy has already earned this Swiss company a paycheck from Novartis, a partnership with MedImmune and success in tackling Respiratory Syndrome.
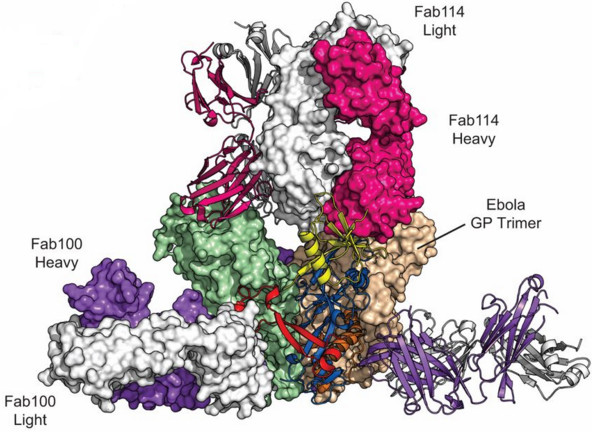
Now Humabs and its partners have discovered two antibodies that can neutralize the Ebola virus. The antibodies (mAb100 and mAb114) were isolated from the blood of two survivors of past Ebola outbreaks (in 1995).
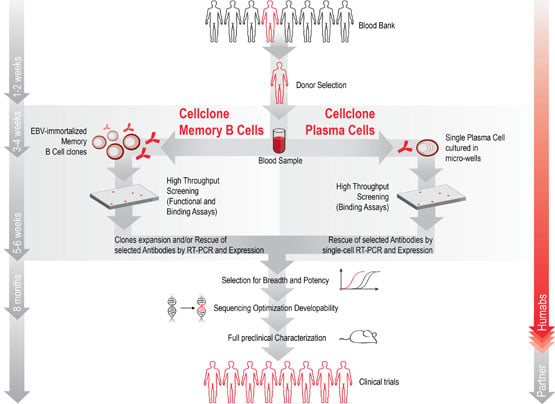
Both antibodies demonstrated high virus-neutralizing capacity, so they went on to be furhter investigated at an academic level.
It’s this work that was recently published in two articles in Science (wow!), one about the antibodies’ mechanism of action and another about the therapeutic potential of mAb114.
mAb114 seems particularly promising, as it attacks previously unknown weakness of the virus. It blocks the binding of the virus to the human cells (a key step in infection) by attaching to an essential glycoprotein of the the virus. This is an effect that has never been described before.
A therapy based on mAb114 is now on the fast track to development, with the support of US’ Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). The next steps are to manufacture the antibody and run clinical tests.
Ebola kills about 50% of people infected, but the survivors carry life-long immunity. This means the virus is a particularly good candidate for the strategy Humabs uses (French HiFiBiO has a similar strategy too).
Since 2014’s Ebola outbreak, a number of companies have devoted resources to finding a preventative vaccine and a cure. Merck also bought a license for a vaccine currently in phase III trials. GSK on the other hand will soon advance their phase II trials (for children and adults) of an in-house vaccine.
The partnership between Bavarian Nordic and Janssen is also initiating a series of trials, including phase III for their vaccine.
In this scenario, it seems unlikely that Humabs will be the first to approve a vaccine for Ebola. But this new antibody is a really promising candidate to treat people already infected.