Newsletter Signup - Under Article / In Page
"*" indicates required fields
This expert has told us why recombinant proteins are an elegant way to go in the production of veterinary vaccines and why glycosylation patterns can play a big part in all of it!
For many decades, human blood plasma has been a source of different biotherapeutic proteins, including antibodies, albumin and blood coagulation factors. Although they are essential for the treatment of different diseases, such as hemophilia or immunological disorders, sources are limited and safety concerns persist.
Fortunately, a lot has been achieved in the field of recombinant technologies in the last 20 years. Today, recombinant proteins in the form of ion channels, antibodies, cytokines, coagulation factors and many more can be produced in the laboratory without the help of human donors. Many of these proteins, however, are hard to manufacture as they have highly complex glycosylation patterns that are difficult to express.
CEVEC is a biotechnology company that has risen to the challenge of tackling the production of these complex recombinant proteins, which they call “proteins previously out-of-reach”. The increasing demand for the efficient manufacturing of difficult-to-express therapeutic proteins in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology and even veterinary sectors suits the company very well.

With its CAP®Go technology CEVEC is able to produce recombinant proteins with specific tailor-made glycosylation patterns, which can improve their physicochemical and pharmacological properties. However, recombinant proteins are not only valuable to human health. Very recently, the company signed a non-exclusive license agreement with a leading European veterinary pharmaceutical company for the use of their protein products in the production of vaccines for livestock animals.
We caught up with Dr. Nicole Faust, CSO of CEVEC, to ask her all about this new project, why difficult-to-express recombinant proteins are useful for veterinary medicine and what challenges CEVEC faces in this field.
Nicole, animal medicine isn’t something we hear a lot about in biotech. Why did you see veterinary medicine as an opportunity?
Interestingly enough, when it comes to immunizing animals the vaccines are not so different from the ones used for human vaccination. Animal vaccines can be attenuated or inactivated viruses, or as in our case, isolated viral proteins. Such proteins provide very safe vaccines because there is no risk of a harmful virus forming accidentally.

Viral protein-based vaccines can be produced with common biotech methods that are also employed for the production of other recombinant proteins. These methods include cell line development, upstream and downstream process development and the production of the recombinant protein in fermentation processes. We have specialized in these technologies, which is why we saw our platform fit to take up this new project in the field of veterinary medicine.
What are the advantages of using CEVEC’s CAP-Go?
Our CAP-Go platform has been specifically designed to address the efficient recombinant production of what we call “proteins previously out-of-reach”. By this we are referring to proteins that are difficult to manufacture with the standard rodent cell-based production systems.
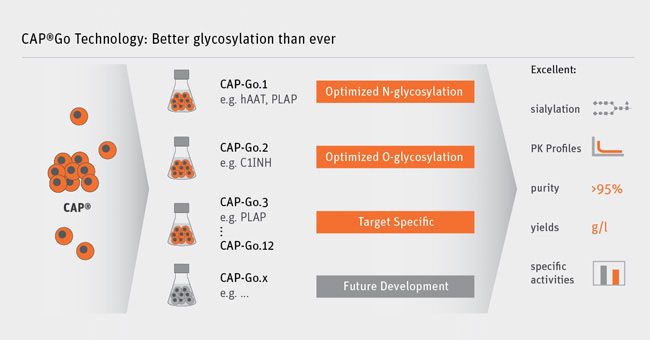
Conventional platforms often have difficulties with low titers or insufficient protein quality, including lack of activity, incorrect processing, degradation or an undesired glycosylation pattern. Our CAP-Go system can overcome these issues. It consists of several cell lines that are all engineered to efficiently produce difficult recombinant proteins.
The platform particularly aids the production of complexly glycosylated proteins, for instance, vital blood coagulation factors, other plasma proteins, viral proteins or enzymes. In addition to generating high yields of the product the platform allows us to tailor the glycans, the sugar structures attached to the glycoprotein, according to specific requirements.
What are the main challenges you are facing in regards to animal medicine?
One of the main challenges in the field of veterinary vaccines is the fact that the market is very price sensitive. As a result, companies engaging in the development and production of these products have to find a cost-effective solution.

In this respect, CEVEC´s CAP-Go platform offers several advantages. For example, the system even provides high yields of proteins that are difficult to manufacture. It also works with full viruses, as we have recently shown in a project for a human Zika vaccine in cooperation with NewLink Genetics.
Additionally, the system is fully scalable allowing for large scale batches and drastically reducing the cost per dose by economy of scale. This enables our partners to manufacture their products in a cost-effective way.
Can you foresee other applications for your CAP-Go platform?
The CAP-Go platform can be very helpful for every application in which the production of complex recombinant proteins is required. I am certainly curious to discover what the future holds.
Recently, a totally different potential application has come up. We have found that CAP cells very efficiently produce exosomes, extracellular vesicles that occur in bodily fluids and are thought to play a role in the transportation of various payloads. Using our cell line development capabilities, this knowledge can be used to generate novel CAP cell lines that can serve as a source of human exosomes carrying various ‘cargoes’ for therapeutic applications.
You can read more about Cevec’s license agreement here or click here to discover more about the technology itself!
Images via Mr.Exen, ArtemZ, MYP Studio/Shutterstock and via Cevec