Red Algae bloom on glaciers during summer, which may give the snow more than a nice pink shade. The darker color makes the glacier melt faster – a previously overlooked mechanism in climate change.
 In biotech, algae almost became synonymous with unlimited potential, including as a promising new generation of biofuels – so they should be pretty environment-friendly, right?
In biotech, algae almost became synonymous with unlimited potential, including as a promising new generation of biofuels – so they should be pretty environment-friendly, right?
Not always, it seems. One of the characteristics that make algae a biotech star is they can produce carotenoids, chemicals that give them a reddish color and are sought-after in medicine and other applications. However, this is also how they are contributing to climate change – and with much more impact than previously thought, say researchers from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, University of Leeds, University of Bristol and Aberystwyth University.
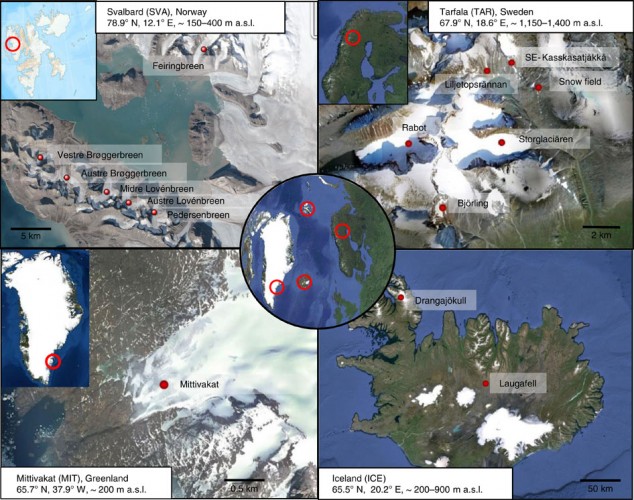
The team of researchers took off to the Pan-European Arctic to study glacial microbiology. Exploring the microbes present in remote environments (such as deserts) is often done for ‘biodiversity mining‘ and getting useful items like omega-3-producing algae or equivalents to rare earths.
Yet here there was another purpose (besides the sheer awesomeness of knowing what grows on the Arctic). The researchers wanted to understand how much these microbes changed the snow’s color.
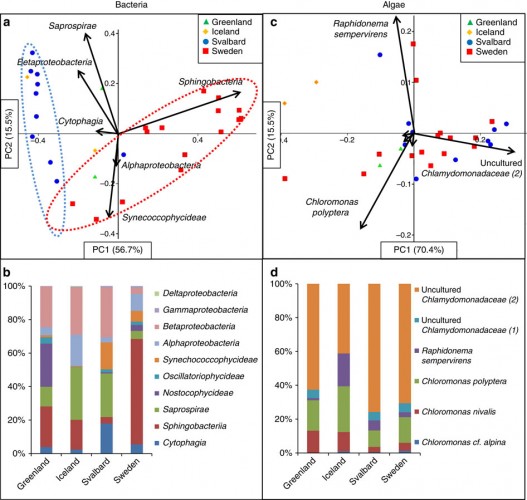
The color of snow is important for its albedo – the fraction of light that is reflected back, instead of absorbed. The darker the snow, the more heat will be absorbed. The albedo of the Arctic is an important part of the climate equation, as well as the models for climate change (that tells us how much the oceans will rise, for example).
The work, published in Nature Communications, shows that red blooms of algae can reduce the albedo by 13%, which has a major impact in how fast the glaciers melt. Also, of course, as the glacier melts more algae grow on the resulting water – a vicious cycle of sorts.
The main conclusion of the study is that we need to change the models used to make climate-related decisions. However, given that it’s mostly one species of algae, I wonder if someone will come up with a algae gene drive similar to those for virus-spreading mosquitoes?
Feature Image Credit: Liane G. Benning/GFZ
Figure 1 and 2 Credit: Lutz et al. (2016) The biogeography of red snow microbiomes and their role in melting arctic glaciers. Nature Communications (doi: 10.1038/ncomms11968)





