TiGenix announces positive one-year results for its phase I/II trial of donor-derived cardiac stem cell therapy in acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
The Belgian biotech TiGenix is developing allogeneic stem cell therapies. Now the company has announced that its cardiac stem cell therapy AlloCSC-01 reached its primary endpoints in a phase I/II trial.
In 2015, the company acquired Coretherapix in a €292M deal for its allogeneic cardiac stem cell pipeline, which is being developed for the treatment of AMI. The first-in-human trial was designed to test the safety and feasibility of an intracoronary infusion of donor-derived expanded cardiac stem cells (AlloCSCs) in patients with AMI and left ventricular dysfunction.
AlloCSC-01 consists of adult allogeneic cardiac stem cells isolated from the heart of donors and expanded in vitro. In vivo studies suggest that these cells have cardio-reparative potential by activating regenerative pathways and promoting the formation of new heart tissue.
The current phase II study demonstrated the safety of these allogeneic stem cells. Initial results also revealed a larger reduction of infarct size in a subgroup of patients.
TiGenix is well known for ChondroCellect, which was the first cell therapy to reach the European market for the repair of knee cartilage. After the company recently withdrew its market authorization for this product, due to a lack of reimbursement, the biotech is focusing on another stem cell therapy, Cx601, in addition to AlloCSC-01. Under development for Crohn’s disease, Cx601 is currently awaiting EMA approval and is in phase III trials in the US.
For a late-stage clinical company, TiGenix has a low market cap of €191M. Even so, the company seems to be doing well these days with the progress of Cx601 and AlloCSC-01.
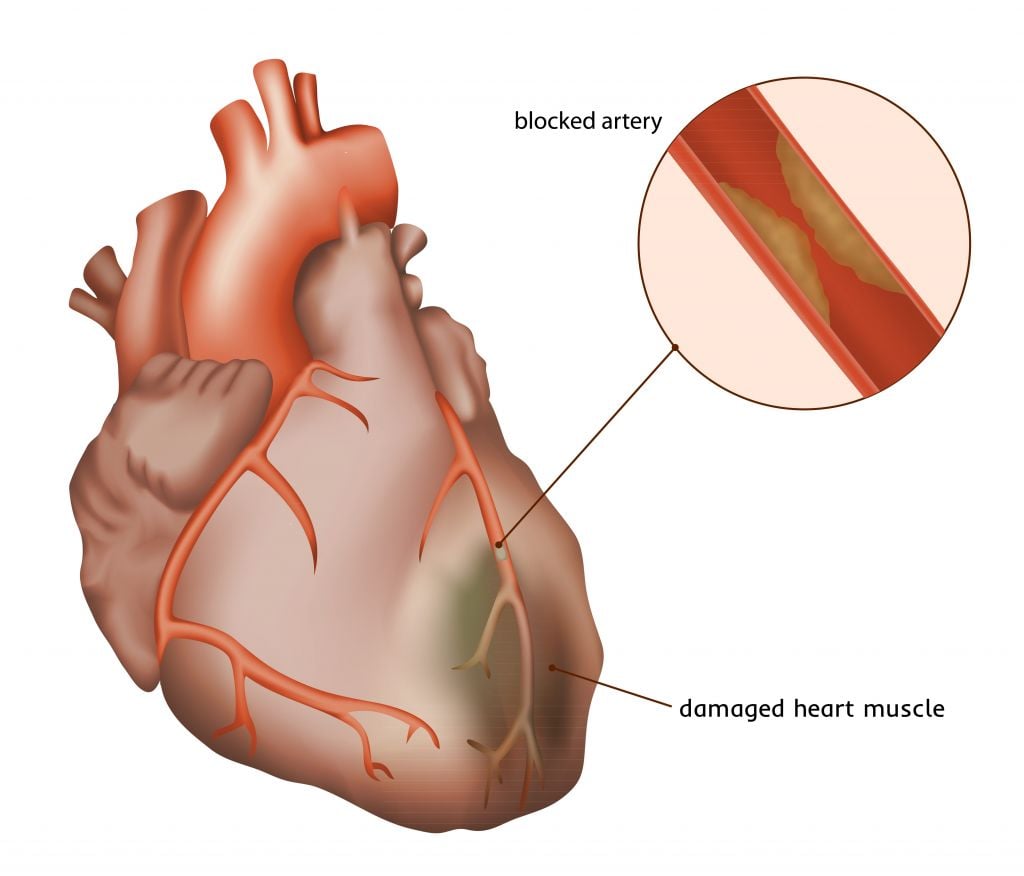
If AlloCSC-01 obtains market approval, it could treat the more than 1.9 million people affected by AMI, a major cause of heart failure. So far, most treatments are palliative or restore myocardial function by angioplasty and insertion of a stent to support the vascular lumen.
Stem cell therapy of the heart is definitely not a new topic, but many trials have been conducted using the patient’s own stem cells derived from the bone marrow. A recent meta-analysis of such trials has suggested that these therapies are safe, but do not enhance cardiac function. TiGenix’s approach using allogeneic heart-derived stem cells may offer a new and promising opportunity in the field.
Images via shutterstock.com / Liya Graphics and Veronika Zakharova