Newsletter Signup - Under Article / In Page
"*" indicates required fields
Media additives, or supplements, are indispensable for cell growth and vitality, as they deliver vitamins, energy sources, and various other essential growth factors. However, current animal-sourced supplements are poorly compatible with GMP regulations critical for cell therapy development and clinical applications. Additives of human origin now present new options.
For the last decades, fetal bovine serum (FBS) has been the standard supplement in cell culture. However, FBS production processes are not thoroughly standardized, making them challenging to use under GMP conditions. In addition, FBS is associated with ethical concerns, as an estimated 2 million bovine fetuses are killed for FBS production each year. New developments include supplements prepared from human platelets – with the potential to overcome the limitations of FBS while enhancing cell growth and performance.
Promoting mesenchymal stem cell differentiation
Cell therapies hold great promise in regenerative medicine. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), for example, are valuable tools in cell therapy because they can differentiate into a multitude of cell types, including bone, cartilage, and heart muscle.
For optimal expansion and therapeutic efficacy, MSCs require a mixture of growth factor proteins and cell adhesion molecules only available in supplements from natural sources. Chemically defined, synthetic media supplements are expensive to produce and must be formulated individually for each cell type.
While FBS contains all components needed, the supplement may be associated with significant health risks. Because FBS is prepared from blood collected from calf fetuses in commercial slaughterhouses, contamination with animal-derived bacteria, viruses, prions, or endotoxins is a common issue.
As with any animal-derived product, bovine proteins may provoke an immunological response in humans, and natural compounds such as sialic acid may promote inflammation and tumor progression.
Challenges of lot-to-lot variation
In addition, the poorly defined FBS sourcing and processing procedures give rise to high lot-to-lot variability that makes FBS supplements challenging to use.

“Researchers buy samples from several lots, test them in their cell culture, and then order a large quantity of the best lot that will last for the next few years – hopefully through the end of their project,” Hatim Hemeda, CEO & Founder at PL BioScience, explained.
While such an approach may work in basic academic research, a stable supply of standardized and well-characterized supplements is indispensable for cell therapy applications.
Platelet lysates: The human alternative
Researchers in Hemeda‘s team at the university hospital in Aachen, Germany, have identified human platelet lysates (HPL) as a high-performance, cost-effective alternative able to overcome the issues associated with FBS. In 2015, Hemeda founded PL BioScience to bring HPL to market.
At PL BioScience, human platelets are sourced from blood donations in certified blood banks. The shelf life for platelets is extremely short – only five days – to exclude any risk of platelet clotting, leading to large quantities of expired platelets.
For HPL production, expired platelets are submitted to several freeze-thaw cycles to release the platelet compounds. The lysates are filtered to remove cell debris, followed by diligent quality evaluations. Over 200 donor units are pooled into large batches to minimize lot-to-lot variation.
Overcoming FBS issues, meeting GMP requirements

While FBS must be sourced from different geographical areas depending on the bovine mating season, blood banks provide a consistent supply of platelet samples and sufficient material to meet the growing demand in academic and clinical environments.
“Blood banks are an ideal source of GMP-compliant raw materials,” said Silke Isenhardt, Field Application Scientist at PL BioScience. “Each human donor is qualified and tested, and blood donation, processing, and storage are carried out under strictly controlled, standardized conditions.”
“Also, our products are ethically sourced and give the valuable platelet donations a ‘second life,’ which many of our customers appreciate,” Isenhardt added.
The ELAREM™ portfolio – from academic research to cell therapy
Meanwhile, PL BioScience has developed a complete portfolio of human platelet lysate variants that support projects from bench to bedside.
Academic customers interested in switching from FBS typically start by using the ELAREM™ Prime product line. “Prime shows a comparable performance as FBS at similar pricing but with all the benefits of an animal-free product,” Nicholas Gouw, Marketing Manager at PL BioScience, explained.
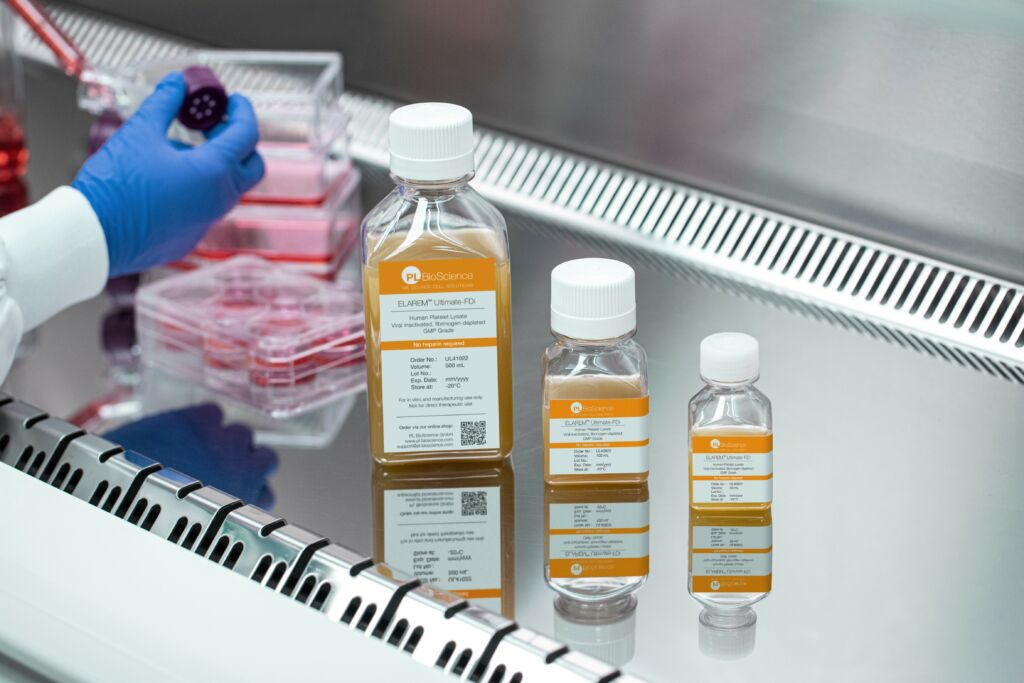
As researchers progress to pre-clinical research, the ELAREM™ Perform HPL supports cell growth at enhanced performance, achieving comparable yields in half the time, with an optional GMP certification.
For the highest safety and regulatory compliance needed in clinical trials and patient therapy, ELAREM™ Ultimate HPL has been developed, offering additional virus inactivation and fibrinogen depletion options.
The patent-protected ELAREM™ Matrix Kit combines HPL nutrients and a viscous scaffold to form a 3D matrix that is more similar to the natural cell environment than a 2D cell culture, making it ideally suited for cell research.
“We are happy to offer a high-performance, GMP-compatible, sustainable, state-of-the-art supplement platform that can support the growing needs of our clients in the years to come,” Gouw concluded.
Interested in animal-free supplements for your cell culture? Connect with PL BioScience to learn more.
Images courtesy: PL BioScience






