Newsletter Signup - Under Article / In Page
"*" indicates required fields
Over 4% of the world’s population suffers from one or more of over 80 autoimmune diseases identified to date. A large variety of treatment approaches has already been developed to curb the detrimental effects of autoimmune diseases, and the market continues to flourish. In fact, it is estimated to reach a staggering value of €7.06B by 2025.
Discover the inflammatory pathways and current and new therapeutic approaches for five of the most common autoimmune diseases!
By the early 20th century, researchers were sure that the human immune system was capable of attacking itself and the cells around it. But they lacked the evidence to prove it. Then, in the 1950s, a series of clinical laboratory experiments started revealing the true nature of autoimmune diseases, when researchers discovered that the immune system can self-harm and be incapable of differentiating between pathogens and its own cells.
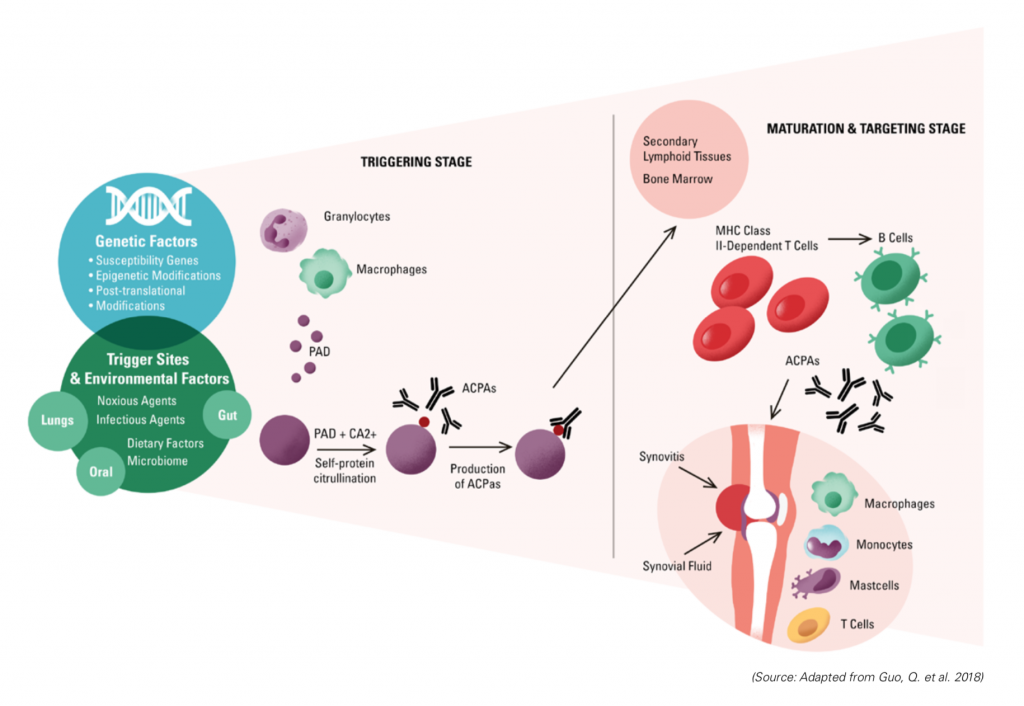
For example, in 1957, E.C. Franklin and colleagues discovered a specific protein in the serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Based on this discovery, the researchers hypothesized that the blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients contained antibodies that reacted with other antibodies as though they were antigens, resulting in the formation of complexes that caused joint inflammation.
Another example is the discovery of insulitis – lymphocyte infiltration resulting in disease – in the pancreas of patients who had died from type 1 diabetes. This discovery came in the 1960s, decades after type 1 diabetes was first reported and even after insulin became available in 1920. Today, it is understood that type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, in which the body’s own immune cells start attacking and destroying insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Similarly, in inflammatory bowel disease, immune cells infiltrate the epithelial layer of the intestine, where they trigger inflammatory cascades, which result in chronic inflammation of the bowels. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease can suffer from one of two types: Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, and ulcerative colitis, which occurs in the large intestine and the rectum.
Although atherosclerosis was historically seen as a lifestyle-triggered disease, research in the last 20 years has shown that it has a strong autoimmune component. The formation of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries has been revealed to be caused by autoimmune mechanisms and inflammatory processes.
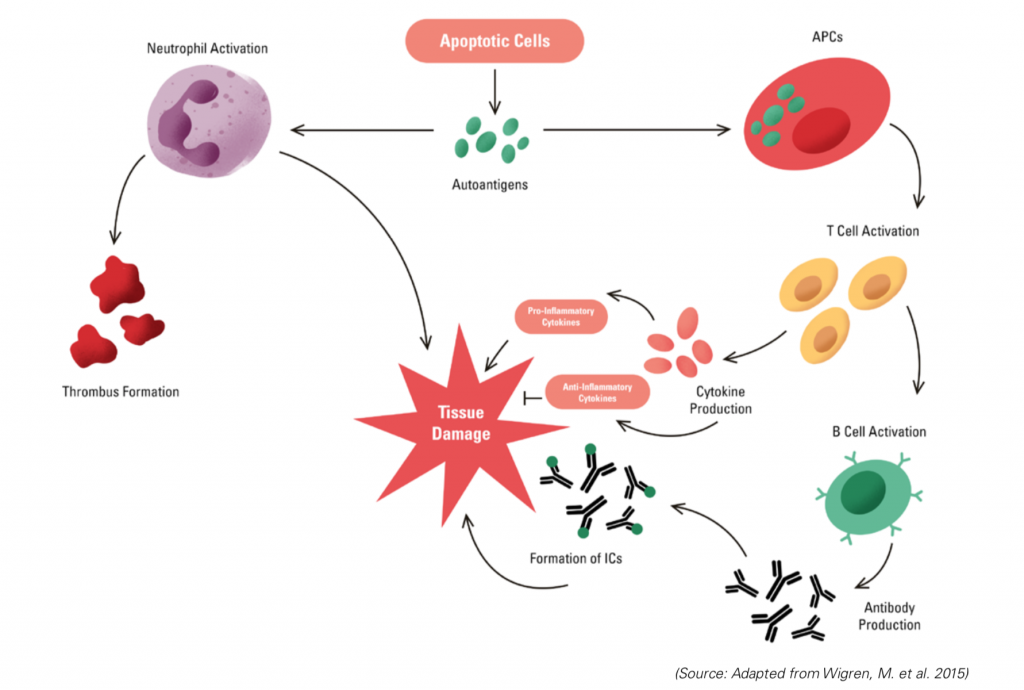
Unlike the other autoimmune diseases discussed above, which are more or less localized, the autoimmune disease lupus can cause widespread inflammation in multiple organs and systems, such as the skin, joints, heart, kidney, lungs, and other internal organs. If left untreated, lupus can result in irreversible damage to internal organs.
Together with PerkinElmer Cisbio, we have created this brand new report that will guide you through the immunological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches of five of the most common autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, type 1 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and lupus. In this report, we take a closer look at current and new therapeutic approaches for these five autoimmune diseases and determine the different inflammatory pathways that can be targeted for the treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases alike.
Images via E. Resko